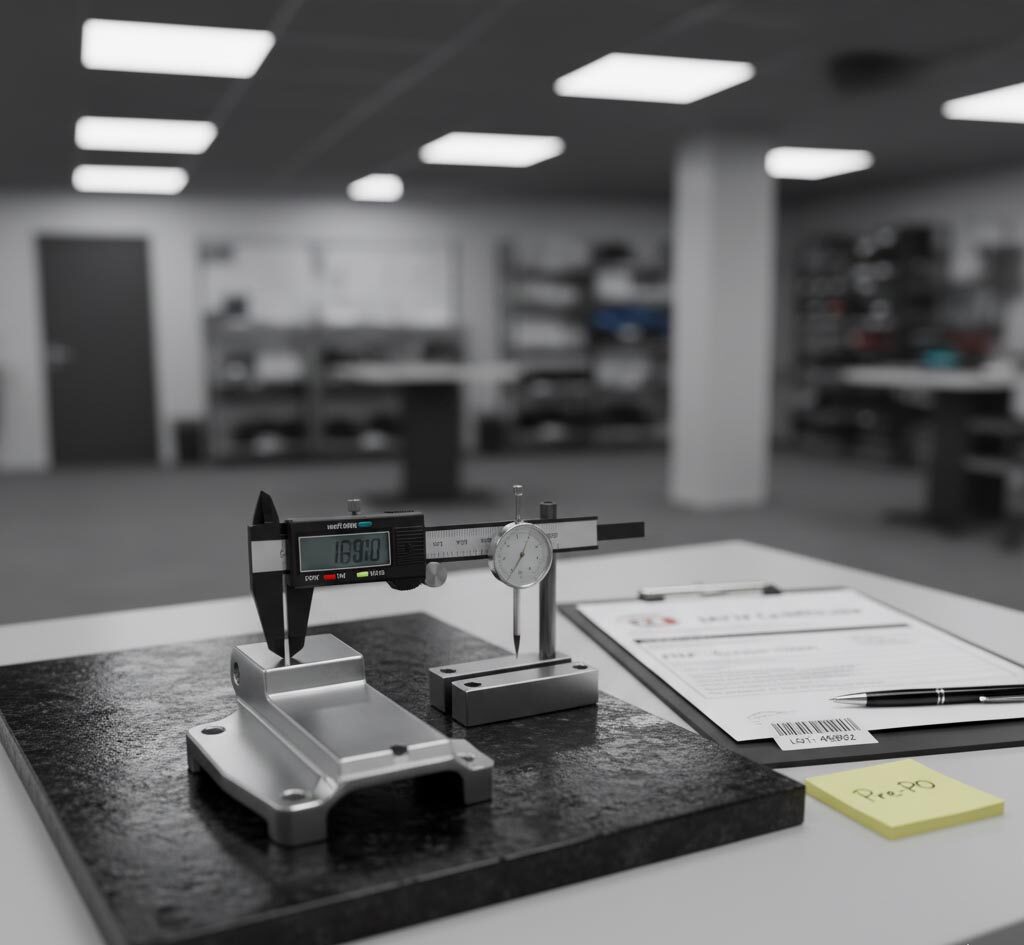

IATF 16949 is the automotive quality backbone. If you buy stamped parts, welded assemblies, or tube-formed components, running a tight pre-PO verification keeps launches smooth and protects you from chargebacks and warranty risk. Use the steps below before you award a purchase order.
1) Validate the Certificate (site • scope • validity • accreditation)

- Site & scope match: Certificate address = quoted plant; scope includes automotive component manufacturing.
- Current & accredited: Check issue/expiry; look for a recognized CB/IAF mark; request latest audit summary (majors/minors & closures).
2) PPAP Level 3 — Proof of Repeatable Production

- Special characteristics flow-down: Symbols carry through PFMEA → Control Plan → gauges/WI.
- Results complete: Full dimensional to drawing rev; material/coating certificates attached.
- Pack & label validation: Photos/specs approved for export and receiving.
3) MSA (GR&R) + Initial Capability — Trust the Gauge, Then the Process
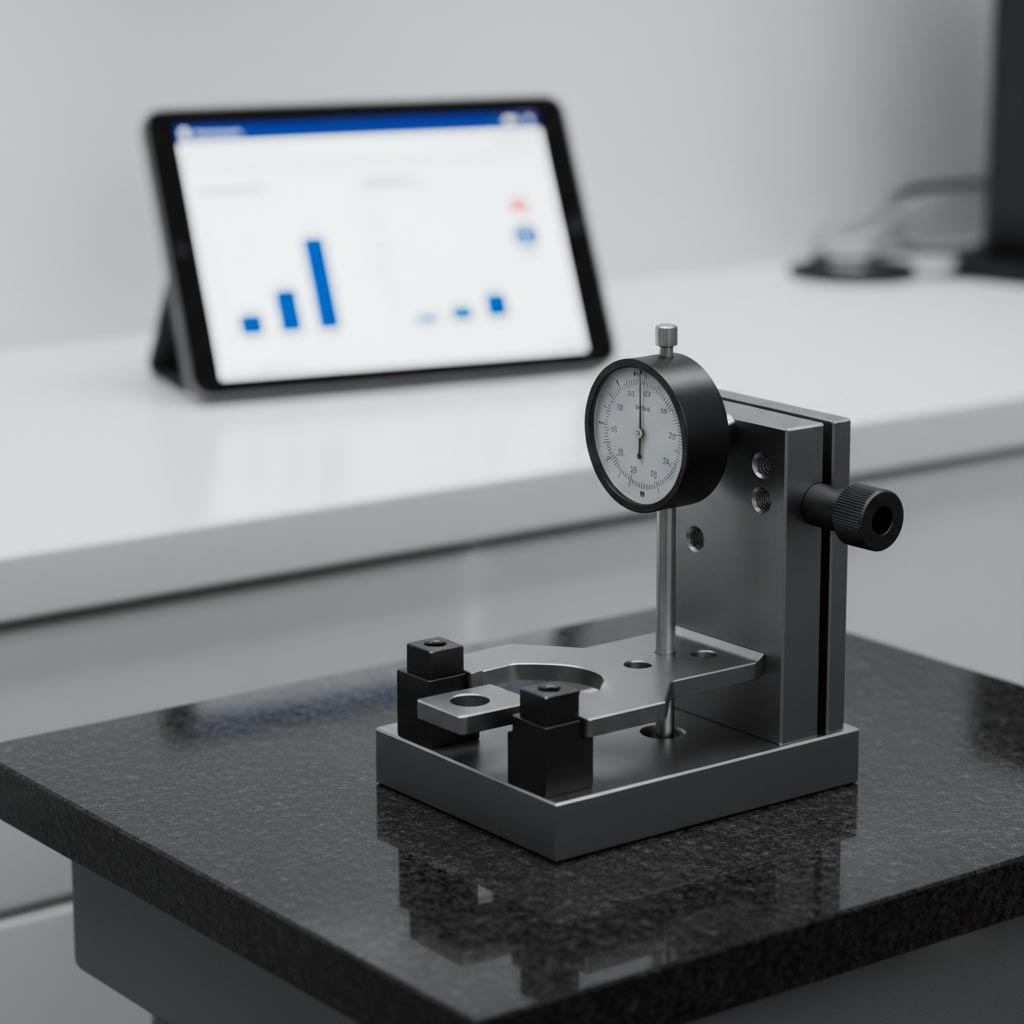

- Gauge acceptance: Variable GR&R meets your criteria; use attribute agreement for visuals.
- Capability data: Provide Cp/Cpk (and Pp/Ppk if required) on CTQs with traceable raw data.
4) Lot Traceability & Export Labels — Recalls and Audits Made Simple

- Lot scheme: Date + shift + press/weld cell recommended; link lots to heat/batch.
- Label format: Code 128/QR per ASN/EDI; include drawing rev and CTQ warnings if needed.
- Export pack: Carton strength, pallet treatment, humidity protection, containerization plan.
Copy-Ready RFQ/PO Clause
Supplier shall maintain a certified IATF 16949 QMS for the quoted site. Provide PPAP Level 3 unless otherwise approved, including PFMEA, Control Plan, MSA (GR&R for critical gauges), initial capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33) on CTQs, traceability scheme (lot/material certs), and packaging validation. Any product/process/material change requires prior written approval and PPAP resubmission.
Quick Buyer Checklist
- IATF certificate valid, accredited, correct site & scope.
- PPAP Level 3 complete; special characteristics aligned; pack & labels validated.
- MSA passed on critical gauges; initial Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33 on CTQs.
- Lot traceability + barcoded labels; export packing spec approved.
Detroit’s Big Three: A Quick Primer
- GM — Diversified portfolio across cars, SUVs, and trucks; large investments in EVs and software-defined vehicles.
- Ford — Icon of assembly-line efficiency and a leader in pickups and commercial vehicles.
- Stellantis (Chrysler) — Global group formed via mergers, stewarding American nameplates alongside European brands.
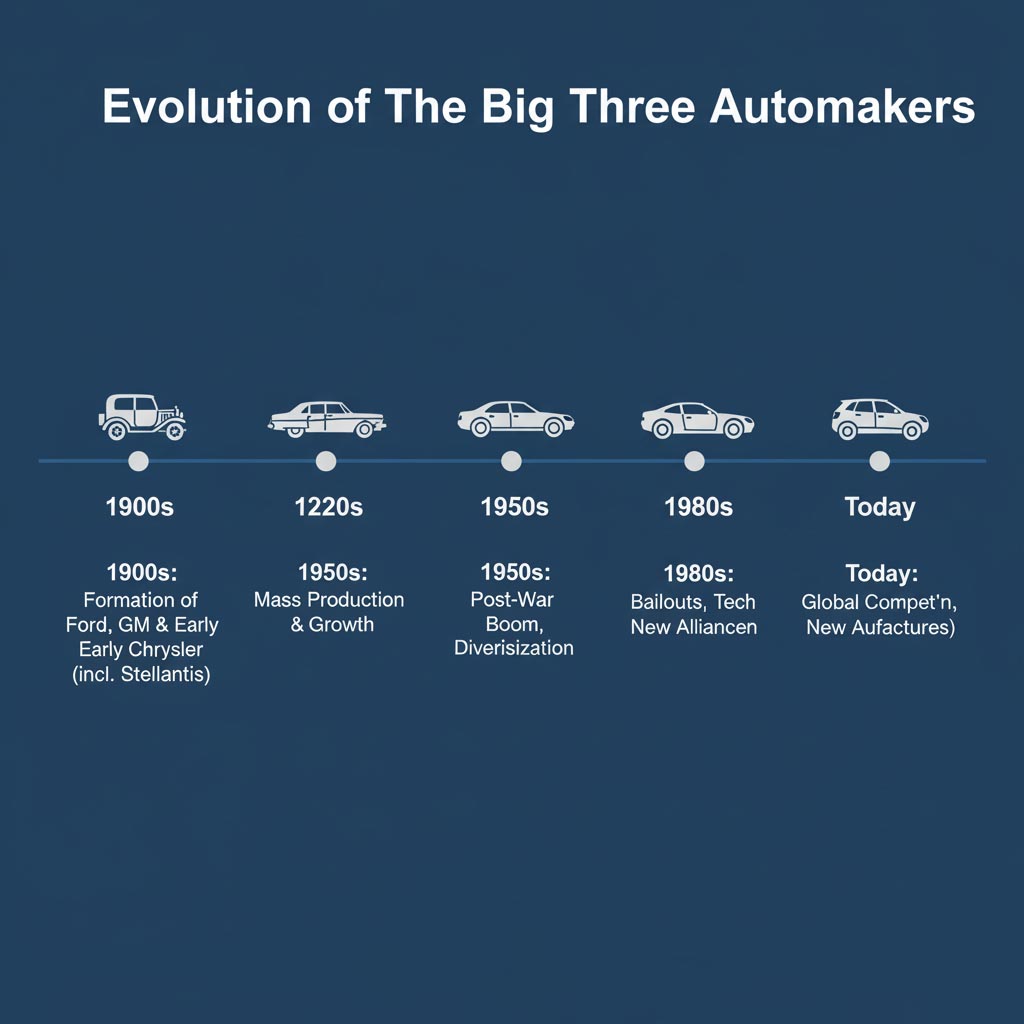
What “Big Three” Means Today
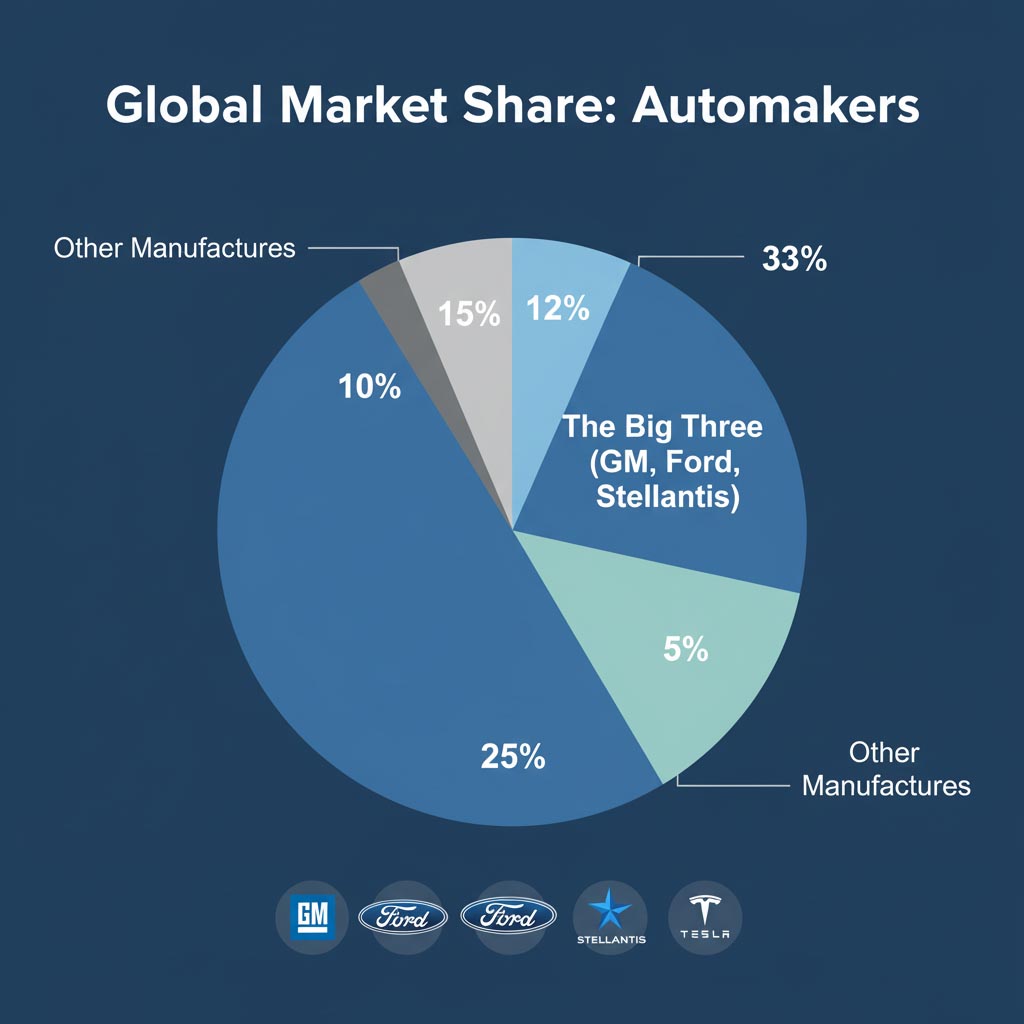
In the U.S., the term still points to GM, Ford, and Stellantis. Globally, however, leadership shifts as production footprints, EV adoption, and new model cycles roll out. Toyota, Volkswagen, Hyundai Motor Group, and others frequently rank among the world’s top manufacturers. The modern market is better described as a Big Many, where software platforms and regional strengths matter as much as scale.
How They Compete in 2025
- Electrification & Software: Heavy investment in EV platforms, battery supply, and over-the-air software.
- Trucks & SUVs: Full-size pickups and SUVs remain profit pillars, funding innovation in ADAS and connectivity.
- Manufacturing Footprint: NA plants are being retooled for flexible ICE/Hybrid/EV production with higher levels of automation.

Key Takeaways
- In the U.S., the Big Three are GM, Ford, and Stellantis.
- Globally, leadership is shared among several groups as EVs and software redefine competition.
- For suppliers, quality, agility, and engineering collaboration determine long-term success.
